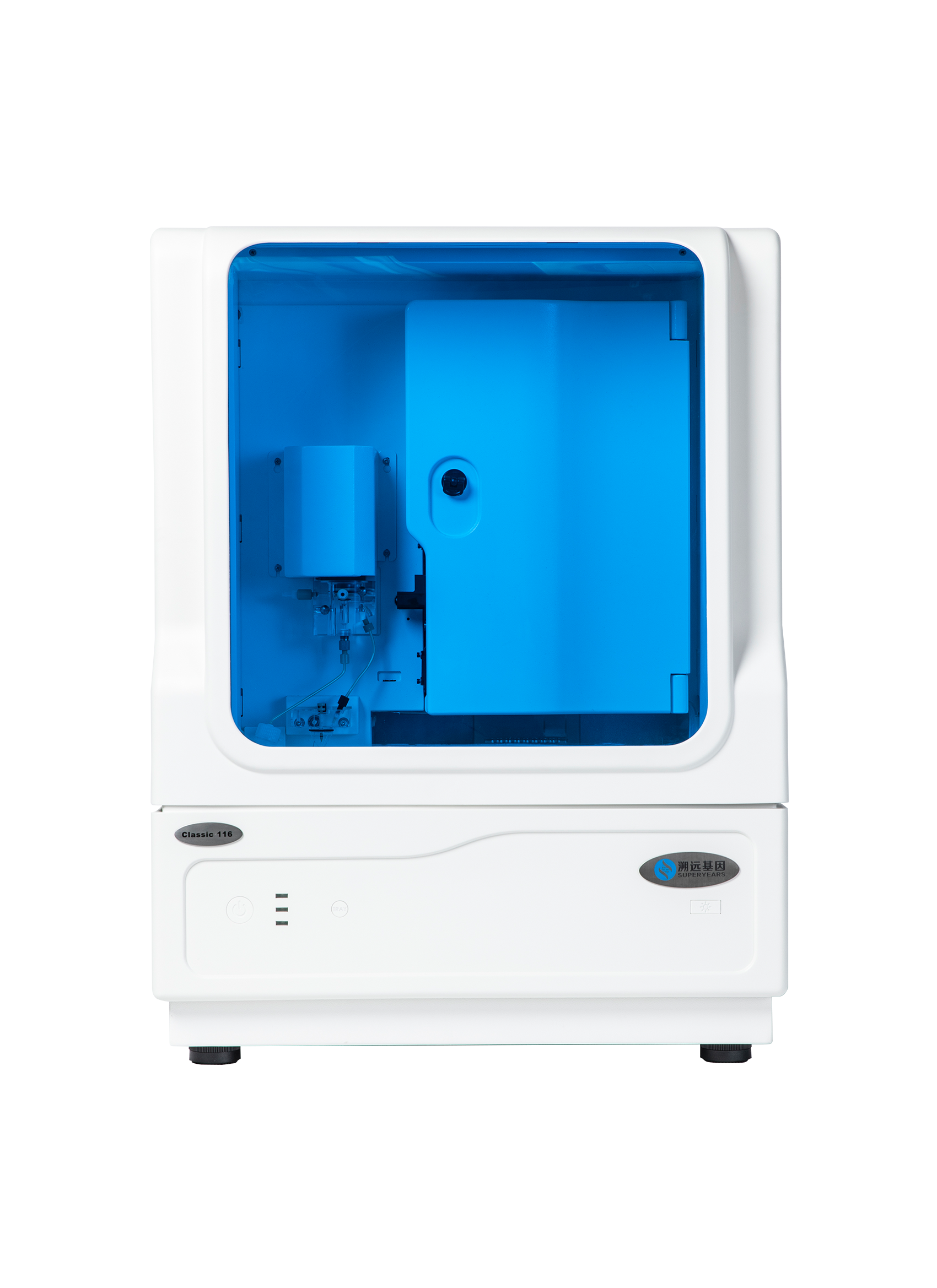
Classic Series Genetic Analyzer
| Size (L x W x H) | Doors Closed:610 x 532 x 812 mm Doors Opened: 1225 x 532 x 812 mm |
| Weight | 95KG (approx.) |
| Channel | 8, 16, 24, 96 (under research) |
| Fluorescence Dye | 6、8 |
| Capillary Length | 36 cm、50 cm |
| Sampling Method | Auto-Sampling, Compatible with 96-well plate(x2) and 8-strip tubes. |
| Polymer-Injection Method | Auto-Polymer Injection |
| Laser | Solid-state semiconductor |
| Laser wave length | 505 nm |
| Fluorescence Dye wave length | > 520 nm |
| Size (L x W x H) | Doors Closed:610 x 532 x 812 mm Doors Opened: 1225 x 532 x 812 mm |
| Weight | 95KG (approx.) |
| Channel | 8, 16, 24, 96 (under research) |
| Fluorescence Dye | 6、8 |
| Capillary Length | 36 cm、50 cm |
| Sampling Method | Auto-Sampling, Compatible with 96-well plate(x2) and 8-strip tubes. |
| Polymer-Injection Method | Auto-Polymer Injection |
| Laser | Solid-state semiconductor |
| Laser wave length | 505 nm |
| Fluorescence Dye wave length | > 520 nm |
| Temp. Accuracy | ΔT≤0.2℃ |
| Resolution Ratio | 0.15 bp |
| Detection Capability | Above 850 bp |
| Fluorescence Dye wavelength | > 520 nm |
| Power | 220±10% VAC,50±1 Hz; Single Phase: 10 A,2200 VA |
| Ambient Temperature | 15℃~30℃, Temperature Uniformity ±2℃ |
| Relative Humidity | 20%~80% |
| Atmospheric Pressure | 86 kPa~106 kPa |
| Operational Mode | Average running time (min) | Max.Flux (Sample/Day) | Capillary Length(cm) | Polymer type | Continuous Reading Length (CRL)(CRL) |
| Sequence36_SY07 | 35 | 656 | 36 | SY07 | 500 bp |
| Sequence50_SY07 | 120 | 192 | 50 | SY07 | 850 bp |
| Fastseq50_SY07 | 60 | 384 | 50 | SY07 | 700 bp |
| Operational Mode | Average running time (min) | Max.Flux (Sample/Day) | Capillary Length(cm) | Polymer type | Continuous | Reading | Length (CRL)
50-400 401-640 640-1200 |
||
| GeneScan36_SY04 | 50 | 448 | 36 | SY04 | 40-640 bp | 640 bp | <0.15 | <0.3 | N/A |
| GeneScan36_SY07 | 35 | 656 | 36 | SY07 | 40-640 bp | 640 bp | <0.15 | <0.3 | N/A |
| GeneScan50_SY07 | 45 | 512 | 50 | SY07 | 40-640 bp | 640 bp | <0.15 | <0.3 | N/A |
| GeneScan50_SY07Long | 125 | 176 | 50 | SY07 | 40-1200 bp | 1200 bp | <0.15 | <0.3 | <0.35 |

Accuracy
“Gold Standard” sequencing, accuracy rate 99.99%

High efficiency
6-color,8-color Fluorescence, and max. of 70 STR loci can be detected in a single test

Economic
Cost-effective product and consumables, Free software update

Compatibility
Open platform, compatible with mainstream reagent kits and consumables

Customizable
Customized interface, easy to interact, handy to operate

Accuracy
“Gold Standard” sequencing, accuracy rate 99.99%

High efficiency
6-color,8-color Fluorescence, and max. of 70 STR loci can be detected in a single test

Economic
Cost-effective product and consumables, Free software update

Compatibility
Open platform, compatible with mainstream reagent kits and consumables

Customizable
Customized interface, easy to interact, handy to operate
Technical Parameter

Technical Parameter
Classic Series Genetic Analyzer
| Size (L x W x H) | Doors Closed:610 x 532 x 812 mm Doors Opened: 1225 x 532 x 812 mm |
| Weight | 95KG (approx.) |
| Channel | 8, 16, 24, 96 (under research) |
| Fluorescence Dye | 6、8 |
| Capillary Length | 36 cm、50 cm |
| Sampling Method | Auto-Sampling, Compatible with 96-well plate(x2) and 8-strip tubes. |
| Polymer-Injection Method | Auto-Polymer Injection |
| Laser | Solid-state semiconductor |
| Laser wave length | 505 nm |
| Fluorescence Dye wave length | > 520 nm |
Consumable Reagent
Consumable Reagent
| Consumable Reagent | Specification Model | Unit | Code |
| 16-Channel Capillary tube | 36 cm | set | SY01C001 |
| 16-Channel Capillary Capillary Array | 50 cm | set | SY01C002 |
| 10x buffer | 500 ml | Bottle | SY01C010 |
| HD formamide | 25 ml | Bottle | SY01C008 |
| SY04 Polymer | 3.5 ml | Bottle | SY01C005 |
| SY07 Polymer | 28 ml | Bottle | SY01C006 |

Product Application
Product Application

| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Clopidogrel | CYP2C19 | Guarantee the safety and effectiveness of Clopidogrel |
| Aspirin | COX1、GP1BA、LTC4S | Evaluation of the resistance risk of Aspirin |
| Warfarin | CYP2C9、VKORC1 | Guidance of the usage measurement of Warfarin |
| Five types of Antihypertensive | ADRB1、CYP2D6、NPPA、CYP3A5、CYP3A4、ACE、CYP2C9 | Rational use of antihypertensive drugs |
| Statins | SLCO1B1、ApoE | Individualized treatment in accordance with the genetype |
| Nitroglycerin | ALDH2 | The instruction of using Nitroglycerin |
| Homocyste ine | MTHFR | High homocysteine levels are associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease |
| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Hepatitis C | Genotyping of hepatitis C virus | Determine the illness,Assist in determining treatment options |
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B virus drug resistance gene | Guidance of using medicine for Hepatitis B |
| Tuberculosis (TB) | Isoniazid resistance gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Guidance of using Medicine for clinic |
| Tuberculosis (TB) | Mycobacterium tuberculosis is resistant to rifampicin | Guidance of using Medicine for clinic |
| Human papillomavirus infection | HPV genotyping | Early detection of HPV infection |
| Multiple respiratory infections | Common a variety of respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract bacteria, virus detection | Auxiliary diagnosis and differential diagnosis of respiratory tract infection |
| HIV/AIDS | Detection of drug resistance genotypes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) | Guidance for medicine using resistance |
| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Glioma | IDH1, IDH2, TERT gene | Classification and prognosis of glioma |
| Non-brainstem glioma/giant cell tumor of bone | H3F3A, H3F3B genes | Assist in the diagnosis of non-brainstem glioma and giant cell tumor of bone |
| Gastrointestinal stromal tumor | KIT gene, PDGFRa gene | Efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Prognostic assessment of disease |
| Breast cance | HER2, PIK3CA, CYP2D6, BRCA1/2 genes | Prediction of disease risk, prognosis and effective treatment plan |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | EGFR, K-RAS, B-Raf genes | Predicting the efficacy of targeted drugs; Prognostic evaluation of disease |
| Colorectal cance | K-ras, B-Raf, n-Ras genes | Prognosis evaluation and medication guidance |
| Targeted drugs/sorafenib, sunitinib, pazopani, bevacizumab, erlotinib, etc | PDGFRβ, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, EGFR, K-ras, B-Raf, PIK3CA, TTF-1, KIT, etc | Guidance for using targeted medicine |
| Chemotherapy drugs/platinum, taxus, fluorine, gemcitabine, purine, etoposide, teniposide, etc | ERCC1, ABCC2, XRCC1, GSTM1, XPD, GSTT1, GSTP1, BRCA1, etc. | Predict drug efficacy and reduce toxic and side effects |
| Irinotecan | UGT1A1 gene | Predict drug efficacy and reduce toxic and side effects |
| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Trisomy 21 syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, superfemale syndrome | Chromosome (13/18/21/X/Y) multiple STR genotyping | Prenatal and prenatal auxiliary diagnosis |
| Duchenne muscular dystrophy | DMD gene exon deletion, and repeat mutation detection | Differential diagnosis, prenatal screening |
| Brittle syndrome | Fragile X syndrome high-risk gene screening | Diagnosis and establishment of diagnosis, prenatal screening |
| Spinal muscular atrophy | Mutation detection of SMN1 and SMN2 genes | Prenatal genetic screening |
| Phenylketonuria | Detection of phenylketonuria gene mutation | Confirming diagnosis and directing treatment; eugenics |
| Deafness | Genetic testing for hereditary deafness | Genetic screening for neonatal deafness |
| Anemia | Detection of missing type α/β thalassemia (MLPA) | The differential diagnosis |
| Wilson's disease | ATP7B gene | Etiological diagnosis and early treatment; eugenics |
| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Adolescent onset of adult type diabetes | GCK, HNF1A, HNF4A, HNF1B, PDX1, NEUROD1 genes | Differential diagnosis of diabetes type and guidance of using medicine |
| Susceptibility to type 1 diabetes | MHC, CTLA4, TSHR genes | The great significant to evaluate the risk of GD |
| Papillary thyroid carcinoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma | RET gene | RET gene mutation is the molecular pathological basis of MTC |
| Multiple endocrine neoplasm | MEN1, RET gene | Prenatal diagnosis and provide the risk evaluation |
| Abnormal lipid metabolism | LDLR, APOB, LPL, ApoC ⅱ, ABCA1, ApoC ⅰ, ApoC ⅲ, ApoC ⅳ, ApoC ⅴ genes | Effective screening of carriers, auxiliary diagnosis, early treatment |
| Diabetes | OCT2、CYP2C9、PPARγ、SLCO1B1 | Personalized guidance of using medication |
| Congenital adrenal hyperplasia | CYP21A2 gene | Auxiliary diagnosis |
| Hyperuricemia, gout | HLA-B 5801 | NCCN guidelines recommend hLA-B 5801 gene testing before allopurinol |
| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Primary test for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | FLT3, KIT, TP53, RUNX1, CEBPA, ASXL1, NPM1, IDH1, IDH2 genes | Assist in diagnosis, medication guidance and prognosis assessment |
| Primary test for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | DNMT3A, SF3B1, U2AF1, SRSF2, EZH2, WT1 genes | Assist in diagnosis, prediction of disease progression and prognosis assessment |
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) | BCR/ABL1, CRLF2, IKZF1, PRPS1, SH2B3, IL7R genes | Assist in diagnosis, prediction of disease progression and prognosis assessment |
| Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) | JAK2, MPL, ASXL1, EZH2, IDH1, IDH2, SRSF2, U2AF1, TP53 genes | Assist in diagnosis and condition evaluation |
| Polycythemia vera (PV) | JAK2, ASXL1, IDH1, IDH2, SRSF2 genes | Assist in diagnosis and prognosis |
| Primary thrombocytopenia (ET) | CALR、MPL、ASXL1、EZH2、SRSF2、U2AF1、TP53、SF3B1 genes | Assist in diagnosis, prognosis and progression |
| Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) | DNMT3A, ASXL1, EZH2, SF3B1, SRSF2, U2AF1, TP53, NRAS genes | Assist in diagnosis, prognosis and progression |
| Lymphocytic lymphoma/Fahrenheit macroglobulinemia (LPL/WM) | MYD88, CXCR4 gene | Auxiliary diagnostic LPL/WM |
| Chronic neutrophil leukemia (CNL) | CSF3R gene | Deterministic molecular abnormalities of CNL and atypical CML |
| Diseases/Drugs | Detection Items | Clinical Significance |
| Parkinson's disease. | 11 Parkinson's disease genes including SNCA | Genetic screening and early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease |
| Depression | CYP2D6 and four other genes | Guidance on antidepressant medication |
| Epilepsy | POLG and four other genes | Guidance of antiepileptic drugs |
| Mania | Two loci on GSK3B and NTRK2 genes associated with antimanic drugs | Guidance of using medicine for mania |
| Meningitis/encephalitis | Simultaneous detection of multiple encephalitis and meningitis pathogens | Etiological diagnosis of encephalitis and meningitis |
| Mental illness | SLC6A2 and 6 other genes | Guidance of using medicine for antipsychotic medication |
Nanjing Superyears Gene Technology Co., Ltd.
Hotline:
Address:
Room 1501, Chengxian Building, No.50 Chengxian Street, Xuanwu District, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province.
Room 1105/F11, Block 3-2B, 88 Pubin Avenue, Jiangpu Street, Pukou District, Nanjing
All rights reserved: Nanjing Superyears Gene Technology Co., Ltd. ICP No. 17065290





 400-677-8378
400-677-8378 LINKEDIN
LINKEDIN CONTACT
CONTACT 